Systematic Testing Solution of PV Inverter
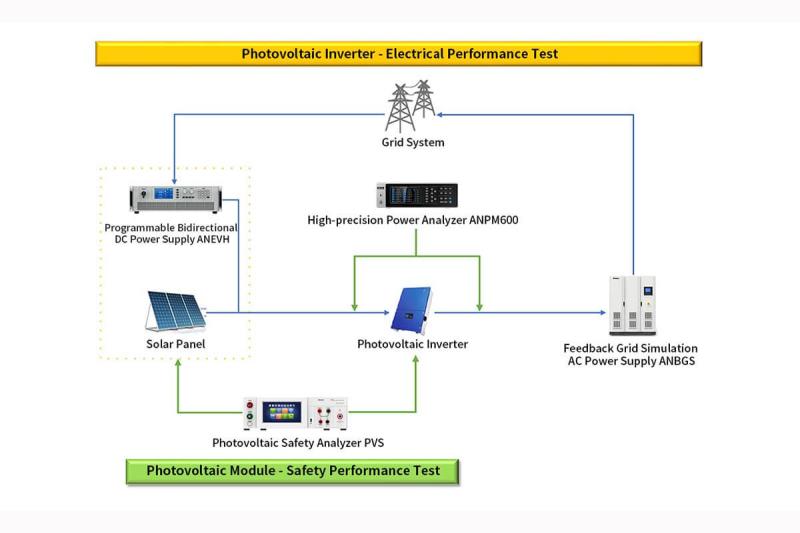
As
the "heart" of a photovoltaic (PV) power generation system, the
performance, efficiency, and reliability of the PV inverter directly determine
the power generation revenue and lifespan of the entire power plant. Therefore,
comprehensive and accurate testing is an indispensable part of every stage of
inverter development, from R&D and production to on-site operation and
maintenance.
The following will systematically explain PV inverter testing solutions from four aspects: testing scenarios, key testing items, core testing equipment and solutions, and development trends.
Core
Testings
R&D
and Verification Testing
Purpose:
To verify the design of new products and ensure they conform to theoretical
models, performance indicators, and various international/national standards.
Features:
Most comprehensive and in-depth testing, the highest precision requirements, and allows
for destructive testing.
Production
and Quality Inspection Testing
Purpose:
To perform rapid and automated functional and performance verification on each
inverter before shipment, ensuring product consistency.
Features:
Fast testing speed, high degree of automation, focuses on pass/fail
determination, and is non-destructive.
Certification
and Type Testing
Purpose:
To obtain market access certificates (such as China CQC, Europe VDE, and North
America UL). Features: Strictly adheres to specific standards (such as IEC
62109, IEC 62116, NB/T 32004, etc.), and is performed by an authoritative
third-party laboratory.
On-site
Installation and Operation Testing
Purpose:
To ensure correct on-site installation, troubleshooting, and to conduct regular
performance evaluations.
Features:
Portable equipment, complex testing environment, emphasis on safety, and basic
functional verification.
Key
Test Items
A.
Electrical Performance Testing
Efficiency
Testing
Maximum
Efficiency: The inverter's efficiency at its optimal operating point.
Weighted
Efficiency (European Efficiency, CEC Efficiency): Calculated by weighting
operating time under different illumination conditions, more accurately
reflecting actual power generation.
MPPT
Efficiency: Measures the inverter's ability to track the maximum power point of
photovoltaic modules, crucial for power generation.
MPPT
Dynamic Performance Testing
Simulates
environments with rapid changes in illumination and temperature to test the
inverter's MPPT algorithm response speed and accuracy.
Power
Quality Testing
Harmonics
and Interharmonics: Analyze the distortion of the output current, which must
comply with standards (e.g., IEC 61727, IEEE 1547).
DC
Injection: Prevent the inverter from injecting DC into the grid,
protecting transformers and equipment.
Power
Factor and Reactive Power Regulation Capability: Test the inverter's ability to
participate in grid regulation at the grid connection point.
Protection
Function Testing
Grid
Connection Protection: Such as over/under voltage, over/under frequency, and
anti-islanding protection. This is the core of safety testing.
Input
Side Protection: DC side overvoltage, reverse connection protection, etc.
Self-Protection:
Over-temperature, over-current protection, etc.
B.
Safety and Compliance Testing
Insulation
Resistance Test: Detect the insulation performance of
the DC and AC sides.
Withstand
Voltage Test (Dielectric Strength Test):
Verify that clearances and creepage distances meet requirements.
Leakage
Current Test: Assess leakage current to ground to
ensure personal safety.
Environmental and Reliability Testing
- Temperature Rise Test: Measure the temperature of critical components under rated load.
- High and Low Temperature Operation/Storage Test: Verify the inverter's adaptability to extreme environments.
- Damp Heat Test, Salt Spray Test, etc.
C.
Grid Support Function Testing (Smart Inverters)
With
increasing photovoltaic penetration, modern inverters need stronger grid
interaction capabilities.
Low
Voltage Ride-Through: In the event of a
grid fault, the inverter cannot immediately disconnect from the grid and needs
to support the grid for a period of time.
Active
Power Derating and Frequency Support:
Adjust output power according to grid commands.
Automatic
Voltage Regulation: Stabilize the grid
connection point voltage by adjusting reactive power.
III.
Core Testing Equipment and Solutions
For
different testing scenarios and projects, the following equipment needs to be
used in combination:
1.
Core Testing Platform: Photovoltaic Simulator + Grid Simulator + Test Analysis
Software
This
is the gold standard for R&D and certification laboratories.
Photovoltaic
Simulator
Function:
Replaces real photovoltaic modules, accurately simulating I-V curves under
different light and temperature conditions, and can simulate complex scenarios
such as shading and aging.
Advantages:
Repeatable, high precision, not limited by weather or site.
Representative
Manufacturers: Ainuo, Keysight, Chroma.
Grid
Simulator
Function:
Simulates various grid conditions, including normal and abnormal conditions
(such as voltage dips and frequency fluctuations), for testing the grid
connection performance and protection functions of inverters.
Advantages:
Can create various test scenarios to verify the grid adaptability of inverters.
Representative
Manufacturers: Ainuo, Keysight, Chroma.
Power
Analyzer
Function:
High-precision measurement of all electrical parameters on the DC/AC side,
including voltage, current, power, efficiency, and harmonics.
Advantages:
High precision (up to 0.01% or higher), the cornerstone of efficiency testing.
Representative
Manufacturers: Ainuo Yokogawa, Keysight.
Automated
Testing Software
Function:
Integrates hardware devices to automatically execute complex test sequences
(such as efficiency curve scanning, LVRT testing) through programming and
generates reports.
Advantages:
Improves testing efficiency, ensures data consistency, and traceability.
2.
Production Testing Solutions
Automated
Testing System: Integrates multiple testing instruments (AC/SOURCE, DC LOAD,
insulation withstand voltage tester, etc.), controlled by PLC or PC, completing
a full inspection of an inverter within tens of seconds to minutes.
Features:
Modular design, high throughput, barcode binding, and data upload to the MES system.
3.
Field Testing Equipment
I-V
Curve Tracker: Tests the I-V characteristics of photovoltaic strings on-site to
troubleshoot component problems.
Power
Quality Analyzer / Portable Power Analyzer: Measures voltage, current, power,
harmonics, etc. at the grid connection point to evaluate actual operating
performance.
General
electrical tools such as insulation resistance testers and clamp meters.
IV.
Development Trends and Challenges
High
Power, High Voltage: With 1500V systems
becoming mainstream, testing equipment requires higher voltage and power
ratings.
Integrated
Energy Storage: The demand for testing
photovoltaic-storage hybrid inverters is surging, requiring the simulation of
more complex charging and discharging scenarios and energy management
strategies.
Higher
Grid Adaptability Requirements: Testing
weak and high-impedance grids presents new challenges.
Digitalization
and AI: Utilizing big data and AI algorithms
to analyze test data, optimize testing processes, and even predict potential
faults.
Increasingly
Stringent Safety Requirements: Testing,
especially DC arcing detection, has become mandatory.
Summary
A
complete photovoltaic inverter testing solution needs to be customized
according to specific testing objectives
(R&D/production/certification/O&M). Its core is an accurate simulation (PV
simulator, grid simulator) and precise measurement (power analyzer). Selecting
mature and reliable testing equipment and solutions is crucial to ensuring
inverter product quality, enhancing market competitiveness, and guaranteeing
the safe and efficient operation of photovoltaic power plants.
Post Your Ad Here
Comments