ECG Gel The Essential Conductor for Accurate Diagnostics and Patient Care
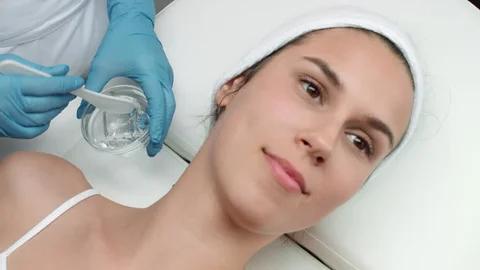
When people think of medical technology, they often imagine sophisticated machines ultrasound scanners, X-ray devices, or heart monitors. But very rarely do they stop to consider the quiet players behind these systems that ensure precision. One such overlooked yet indispensable element is ECG Gel.
This simple, conductive gel doesn’t get the recognition it
deserves, yet without it, even the most advanced ECG machines would fail to
deliver reliable results. Just as ultrasound gel enables sound waves to
travel clearly into the body, ECG gel ensures that electrical signals
from the heart flow seamlessly to electrodes for interpretation.
Let’s uncover the critical role this gel plays, the science
behind it, and why medical professionals must choose it wisely.
Why ECG Gel Exists
An electrocardiogram (ECG) measures the electrical activity
of the heart through electrodes placed on the skin. But here’s the problem:
human skin isn’t a perfect conductor. Natural oils, sweat, and microscopic hair
create resistance, leading to “noise” in readings.
That’s where ECG gel comes in. Applied between the
electrode and the skin, the gel:
- Reduces
electrical resistance by creating a direct conductive bridge.
- Prevents
interference from external static and body hair.
- Delivers
accuracy by ensuring electrodes pick up even faint electrical signals
from the heart.
Without the gel, cardiologists risk false interpretations something
that can have serious consequences when diagnosing arrhythmias, heart
blockages, or cardiac stress responses.
ECG Gel vs. Ultrasound Gel: A Subtle but Crucial Difference
It’s easy to confuse ECG gel with ultrasound gel since they appear similar transparent, slightly viscous, and packaged alike. But their functions are different:
- ECG
Gel: Optimized for conductivity, not for sound wave transmission. It
is usually thinner, spreads easily, and doesn’t dry too quickly.
- Ultrasound
/ Sonography Gel: Formulated for acoustic clarity. Its viscosity is
higher to ensure a stable barrier between transducer and skin, enabling
uninterrupted wave transmission.
Interestingly, both belong to the broader family of ultrasonic
gels, but their applications set them apart. An ECG without conductive gel
risks inaccuracies, while a sonography scan without gel risks blurred images.
Both cases remind us that the gel, though secondary to the machine, is central
to precision.
The Science of Conductivity
Behind its simple appearance, ECG gel carries a careful scientific formulation. Typically water-based, it contains electrolytes that enhance electrical conduction. Unlike oils or creams, it doesn’t leave an insulating layer that blocks signals.
Key properties of a high-quality ECG gel include:
- Non-irritant
and hypoallergenic – safe for long-term use during stress tests.
- Water-soluble
– easy cleanup without residue.
- Non-drying
formula – prevents interruptions during extended monitoring.
- Electrolyte
balance – ensures maximum conductivity without corroding electrodes.
This formulation is what makes the difference between a
clean, readable ECG strip and one full of noise and misinterpretations.
Applications Beyond ECG
Though its name emphasizes cardiology, ECG gel has versatile uses across medical fields:
- Stress
Tests: Continuous monitoring while patients walk or run requires gel
that remains stable without drying.
- Defibrillator
Pads: Ensures maximum contact between paddles and skin during
emergency shocks.
- TENS
Therapy: Used in physiotherapy devices for pain relief to improve
electrode conduction.
- EEG
& EMG: Brain and muscle electrical monitoring also benefit from
conductive gels.
Meanwhile, in the imaging world, ultrasound gel and sonography
gel dominate but the principle is the same: without these mediums, machines
struggle to do their job effectively.
The Challenges with Conductive Gels
As simple as it may seem, even ECG gel isn’t free from challenges:
- Infection
Control: Shared bottles can pose hygiene risks if not handled
carefully. Many hospitals now prefer single-use sachets.
- Patient
Comfort: Gels that feel too sticky, cold, or irritating can make
patients uncomfortable, especially during prolonged tests.
- Residue
Issues: Poor-quality gels may leave behind residue that requires extra
cleaning of both electrodes and skin.
- Shelf
Life: Like any consumable, expired gels lose effectiveness, yet stock
management often goes unnoticed.
These small issues, if ignored, can compromise not just
diagnostic accuracy but also the patient experience.
Innovations in ECG Gel
Medical suppliers are constantly refining ECG gels to meet modern demands:
- Hypoallergenic
blends for sensitive patients.
- Temperature-neutral
gels to reduce the discomfort of a cold application.
- Single-use
sterile packs for infection prevention.
- Eco-friendly
packaging that reduces medical plastic waste.
These advances show how even a small consumable can evolve
to improve healthcare standards.
Why Choice of Gel Matters in Healthcare
Hospitals often prioritize machines over consumables, but in diagnostics, small details change outcomes. Choosing the right ECG gel ensures clarity, efficiency, and patient comfort. When paired with quality ultrasound gel and sonography gel for imaging, healthcare providers create a seamless diagnostic ecosystem where accuracy isn’t left to chance.
Patients may never remember the brand of gel used on them,
but they will remember whether their procedure felt smooth, precise, and
professional. For hospitals, these invisible details translate into trust and
credibility.
Final Thoughts
In a world where medical technology often overshadows its
supporting cast, ECG gel stands as a quiet but vital partner in
diagnostics. It may not flash lights or make sounds, but it bridges the gap
between human biology and medical machinery with silent efficiency.
From the cardiology lab to the sonography room, gels whether
conductive for ECG or acoustic for ultrasound are the unseen conductors of
clarity. And in healthcare, clarity saves lives.
So next time you see a bottle of ECG gel tucked
beside an electrode pack, remember: it may look ordinary, but its role is
extraordinary.
Post Your Ad Here
Comments