Snoring: Symptoms, Causes & Remedies
by James Denlinger Digital Marketing Strategist What is Snoring?
What is Snoring?
 What is Snoring?
What is Snoring?Snoring is one of the most common conditions encountered by mankind. It refers to the sound released by a person when air moves past the throat as one sleeps. While almost every one of us has snored at one point or another, for some, it could be a chronic condition. While occasional snoring is not problematic, it is just enough to frustrate those sleeping beside you.
However, if you have a chronic condition, it can mess with the sleep patterns of those who sleep near you. Also, it can disturb your sleep as well. For people with this chronic condition, medical help may be required. It is generally believed that snoring tends to occur more in men and those who are obese. Unfortunately, snoring can also increase as one gets older.
Some remedies may cure the condition, such as losing weight, drinking more water and avoiding alcohol nearer to your bedtime. For severe problems, there are devices and even surgical remedies available.
Snoring Symptoms
Some of the most common symptoms include the hoarse sound while sleeping, poor cognition, headaches during the day and general sleepiness. Let’s take a look at some of the warning signs of snoring.
- Daytime sleepiness
- Choking or gasping in sleep
- Lapses in breathing
- Morning headaches
- Poor cognition
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
More popularly referred to as OSA, this sleep disorder is often linked with snoring. While not all those who snore have OSA, it could be a possibility, especially if specific symptoms are observed. These include choking at night, poor concentration, morning headaches, chest pains or high blood pressure. If this occurs, then it could be an indication of OSA. It is recommended that the patient immediately visits a doctor. Snoring vs. sleep apnea is a popular subject. However, they go hand in hand and one can lead to the other or act as a symptom.
Poor Concentration
With snoring all night long, it could affect your concentration abilities during the day, leading to poor cognition.
Headaches
Sleep deprivation can cause headaches the next morning. This can even last throughout the day until the person gets their full rest.
Daytime Sleepiness
Of course, when you tend to break your sleep with snoring, you may not get your complete sleep. This could result in sleepiness the next day, not allowing you to focus well on the task at hand, either at school or work.
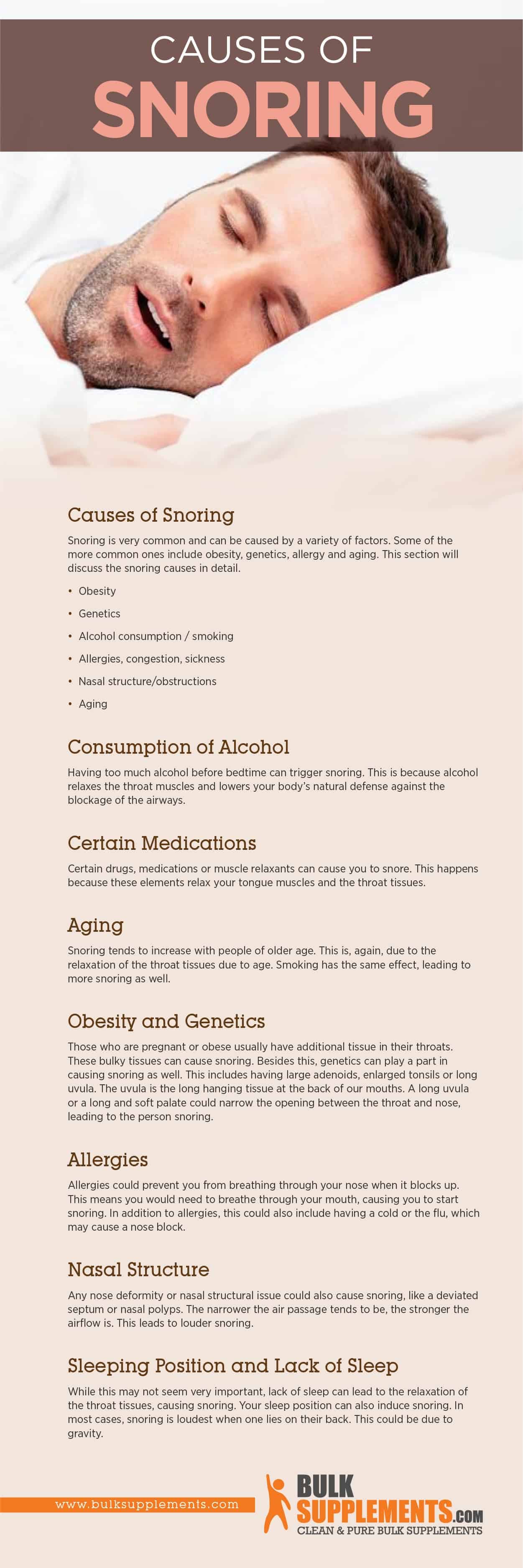
Causes of Snoring
Snoring is very common and can be caused by a variety of factors. Some of the more common ones include obesity, genetics, allergy and aging. This section will discuss the snoring causes in detail.
- Obesity
- Genetics
- Alcohol consumption / smoking
- Allergies, congestion, sickness
- Nasal structure/obstructions
- Aging
Consumption of Alcohol
Having too much alcohol before bedtime can trigger snoring. This is because alcohol relaxes the throat muscles and lowers your body’s natural defense against the blockage of the airways.
Certain Medications
Certain drugs, medications or muscle relaxants can cause you to snore. This happens because these elements relax your tongue muscles and the throat tissues.
Aging
Snoring tends to increase with people of older age. This is, again, due to the relaxation of the throat tissues due to age. Smoking has the same effect, leading to more snoring as well.
Obesity and Genetics
Those who are pregnant or obese usually have additional tissue in their throats. These bulky tissues can cause snoring. Besides this, genetics can play a part in causing snoring as well. This includes having large adenoids, enlarged tonsils or long uvula. The uvula is the long hanging tissue at the back of our mouths. A long uvula or a long and soft palate could narrow the opening between the throat and nose, leading to the person snoring.
Allergies
Allergies could prevent you from breathing through your nose when it blocks up. This means you would need to breathe through your mouth, causing you to start snoring. In addition to allergies, this could also include having a cold or the flu, which may cause a nose block.
Nasal Structure
Any nose deformity or nasal structural issue could also cause snoring, like a deviated septum or nasal polyps. The narrower the air passage tends to be, the stronger the airflow is. This leads to louder snoring.
Sleeping Position and Lack of Sleep
While this may not seem very important, lack of sleep can lead to the relaxation of the throat tissues, causing snoring. Your sleep position can also induce snoring. In most cases, snoring is loudest when one lies on their back. This could be due to gravity.
Risk Factors
There are many risk factors that could cause snoring. Some of the more important ones are discussed in this section.
Gender
It is generally believed that men are more likely to snore than women. Chances are also higher of men suffering from sleep apnea than women. This is not to say that women don’t snore, it just means that men are at higher risk of snoring. Age is another factor that increases the risk of snoring, seen in both men and women.
Obesity
Being overweight can cause people to snore due to extra tissue in the throat. This could also lead to having obstructive sleep apnea or OSA. One reason loud and frequent snoring should never be ignored is because this could be a symptom of sleep apnea, which increases the risk of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular issues.
Alcohol and Smoking
The more one smokes and drinks alcohol, the higher the chances of snoring. Since snoring affects not only you but those who sleep near you, it is advisable to not smoke or drink nearer to your bedtime.
Genetics
Having a family history of OSA leads to an increased risk. Besides this, having large tonsils or a long soft palate can also increase the risk of snoring.
Nasal Conditions
This includes structural issues in the airway, such as frequent congestion or a deviated septum. Deviated septum snoring is quite common and can be fixed easily with a visit to your doctor.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is an important step, no matter what the health issue may be. First, your doctor will want to know the symptoms, the intensity of your snoring, the frequency and any other accompanying symptoms, such as headaches. A physical examination is a routine process in such cases. Your family may be asked about the severity of the problems as well. The diagnosis could be done several ways.
Imaging
Imaging tests, such as an MRI or magnetic resonance imaging, an x-ray or a tomography scan might be advised. This will help the doctor in understanding the structure of your airways and identify if any problems exist. For instance, imaging tests can diagnose a deviated septum.
Sleep Studies
If the snoring is severe, your doctor may recommend a sleep study. This could be done either at your home or at the lab. If your snoring is accompanied by other health issues, the doctors may advise polysomnography. This is an analysis of your breathing while you sleep. In this, many factors are recorded, including your blood oxygen level, heart rate, brainwaves, sleep patterns, breathing rates and more.
Snoring Remedies and Supplements
Snoring is pretty common. You don’t need to visit a doctor if it is only light and occasional. In that case, you can follow some of the remedies discussed here in this section. These natural snoring remedies should be easy to follow as well.
- Garcinia Cambogia – one dose of 500 mg, thrice a day
- Plantain Leaf – one dose of 800 mg, once a day
- Peppermint– one dose of 700 mg, twice a day
Follow Good Sleep Hygiene
Having a good sleeping pattern can ensure you go to bed in a fresh state of mind. For instance, if you tend to work long hours, by the time you get to bed, you are exhausted. This will relax the throat muscles, triggering what we know as snoring. Sleeping with the mouth open could also result in snoring.
Herbal Remedies
Consuming plantain leaves, peppermint and other supplements, either in its natural form or as a supplement, may be able to help relieve cases of snoring. Peppermint can be used in tea or its oil can be used in a dehumidifier.
Clear Nasal Passages
Since ensuring your nasal passages are open, the air will move slowly so that you don’t snore. A hot shower before you go to bed could give you some relief. Nasal strips could also help with this. Snoring aids can also come to the rescue at times.
Sleeping Position
Lying on your back will cause your soft palate to move against the back of your throat. Sleeping on your sides is a good way to deal with it. If you want to stop snoring, another option you can try is to prop yourself up on several pillows or cushions as this will help open up the nasal passages, improving the flow of air.
Pillows and Sheets
It is also a good idea to change your pillows and bed covers regularly as the dust mites in them could cause allergic reactions. If you have pets, do not allow them to sleep on the bed as this could lead to you breathing in pet dander.
Drink Water
Drinking a lot of water can help your nasal areas remain clear and clean, reducing the chances of snoring. A dry throat could also lead to snoring and general discomfort. It is said that men should drink about 16 cups of water every day while women require 11 cups.
Lose Weight
Those who are not overweight snore as well. However, if you have recently started snoring with an increase in weight, working out can solve some issues. This will also ensure you have a good sleep at night.
The Bottom Line
Snoring is the rough sound that escapes from us while we are sleeping. It can be caused due to age, nasal issues, genetics, poor bedtime routine, consumption of alcohol and allergies. Its symptoms include poor cognitive abilities, headaches and sleep apnea. Treatment can range from simple home remedies and supplements to lab tests, snoring aids and even surgeries. Staying hydrated, losing weight and sleeping in a clean environment can all help tremendously.
Sponsor Ads
Created on Mar 6th 2020 13:40. Viewed 415 times.



