Alternatives to Heart Bypass Surgery
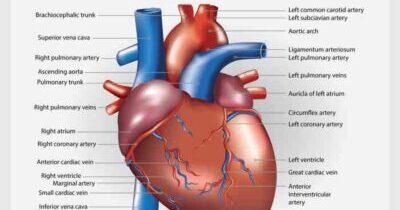
There are alternative treatments to heart bypass surgery, depending on the specific condition and severity of the heart disease. Here are some alternative treatment options:
Medications: In some cases, medications can be used to manage heart disease. These may include drugs to control blood pressure, lower cholesterol levels, reduce blood clotting, and manage symptoms such as chest pain (angina).
Angioplasty and Stenting: Angioplasty is a minimally invasive procedure where a catheter with a small balloon is used to open narrowed or blocked arteries. A stent, a small mesh tube, may be placed in the artery to keep it open and improve blood flow. This procedure can help restore blood flow without the need for open-heart surgery.
Enhanced External Counterpulsation (EECP): EECP is a non-invasive treatment that involves using inflatable cuffs wrapped around the legs to improve blood flow to the heart. It is often used for individuals with chronic stable angina who are not suitable candidates for invasive procedures.
Transmyocardial Revascularization (TMR): TMR is a surgical procedure that creates channels in the heart muscle to improve blood flow. It is typically considered for individuals with severe angina who are not candidates for other treatments.
Therapeutic lifestyle changes: Lifestyle modifications can play a crucial role in managing heart disease. This includes adopting a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, quitting smoking, managing stress, and maintaining a healthy weight.
What is EECP Heart treatment ?
EECP stands for Enhanced External Counterpulsation, and it is a non-invasive treatment for certain heart conditions, primarily chronic stable angina. It is also sometimes referred to as EECP heart treatment.
During an EECP session, the patient lies on a table, and large inflatable cuffs are wrapped around the patient's calves, thighs, and buttocks. These cuffs are connected to a computerized control unit. The cuffs inflate and deflate in a synchronized manner with the patient's heartbeat.
The inflation of the cuffs occurs during diastole, the resting phase of the heart's pumping cycle. By inflating the cuffs, external pressure is applied to the lower extremities, which increases blood flow to the heart. When the heart enters systole, the cuffs deflate, allowing the blood to flow more easily from the heart.
This process aims to improve blood flow to the heart muscle, enhance the delivery of oxygenated blood, and promote the development of collateral blood vessels. Collateral vessels are small blood vessels that can develop over time to create alternative pathways for blood to reach the heart muscle in the presence of blocked or narrowed arteries.
EECP is typically administered as a series of outpatient sessions lasting about one hour each. A full course of treatment usually involves around 35 sessions, typically delivered over several weeks. The treatment is generally well-tolerated and non-invasive, and patients can resume their normal activities immediately after each session.
EECP is primarily used for individuals with chronic stable angina who experience chest pain or discomfort due to reduced blood flow to the heart. It is often considered when other treatments, such as medications or invasive procedures like angioplasty or bypass surgery, are not suitable or have not provided sufficient relief.
It's important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine if EECP is an appropriate treatment option for your specific condition.
What is TMR ?
TMR stands for Transmyocardial Revascularization, which is a surgical procedure used to treat certain types of heart disease, particularly severe angina (chest pain) that has not responded to other treatments.
During a TMR procedure, the surgeon creates channels or tiny channels directly in the heart muscle using a laser or other energy sources. These channels allow blood from the heart's chambers to flow directly into the heart muscle, bypassing the blocked or narrowed arteries.
There are two main techniques used in TMR:
Laser TMR: In this technique, a high-energy laser is used to create the channels in the heart muscle. The laser energy seals the channels to prevent bleeding. The procedure can be performed using different types of lasers, such as carbon dioxide (CO2) lasers or holmium:yttrium-aluminum-garnet (Ho:YAG) lasers.
Non-Laser TMR: Instead of a laser, other energy sources like radiofrequency or microwave energy can be used to create the channels in non-laser TMR.
The channels created during TMR help improve blood flow to the heart muscle and reduce the symptoms of angina by providing an alternate pathway for blood supply. Additionally, the channels may stimulate the growth of new blood vessels (collateral circulation) in the heart, which can further enhance blood flow.
TMR is typically considered for individuals with severe angina who have not responded to other treatments like medications, angioplasty, or bypass surgery. It may be an option when bypass surgery is not feasible due to multiple blocked arteries or other medical conditions.
It's important to note that TMR is not a curative procedure and may not be appropriate for all patients. The effectiveness and suitability of TMR should be evaluated by a healthcare professional based on an individual's specific condition and medical history.
Post Your Ad Here
Comments