All We Need to Know About 1D & 2D Barcode Readers
Every industry or organization makes use of the barcode technology today irrespective of its size. Barcodes look exactly like it is a simple combination of strips and spaces, but they provide the vital product information. In order to decode these barcodes, we make use of the special devices like scanners. The barcode scanners use photosensors to read the barcodes and then convert them into a readable text that is then displayed and stored on a computer or laptop. It may appear to be a very long process, but it simply takes up few milliseconds.
Barcode scanners are widely being used today. They are popularly being used across various industry verticals such as manufacturing, warehousing, education, healthcare, and field service. Their high utility aspect and the popularity of the scanners have introduced many varieties.
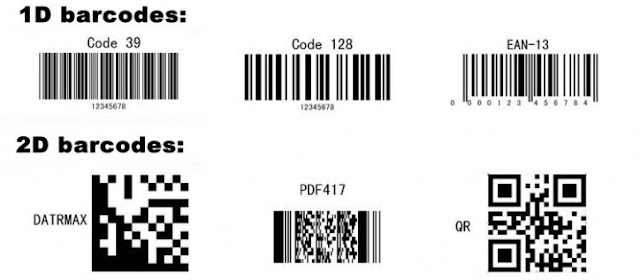
To choose the right barcode scanner is very important for running a business successfully. Prior to doing a selection of the barcode scanner, there is need to know various types of barcodes. The two main types of barcodes are 1 dimensional (1D), or linear barcodes, and 2 dimensional (2D) barcodes.
1D or linear barcodes are used to represent data in black vertical lines. Whereas the two-dimensional (2D) barcodes are represented in many different patterns such as squares, dots, hexagons and other geometric patterns. A 2D barcode can potentially store a greater amount of data as compared to a 1D barcode. A single 2D barcode, that has size about a large postage stamp, can store thousands of alphanumeric characters. This feature can make them more advantageous than 1D. However, 2D barcodes can be easily and accurately read.
The first thing you need to know is that a 1D scanner cannot scan the 2D barcodes, but 2D scanners can easily scan both 1D and 2D barcodes. A 2D barcode scanner can read all these barcode symbology’s along with linear barcodes, such as Code 128, UPC.
The scanner varieties of both 1D & 2D barcode readers are distinguished by their form factor and scanning technologies. The major difference in their form factors lies in the amount of operator manipulation required. The various scanners are as follows wand or pen-style scanners, fixed-mount scanners, and handheld scanners. The handheld scanners are very well available in the scanning technology such as laser scanners, CCD scanners, that are also called the linear imagers. The scanning technology can only be chosen based on the application and requirements.
Advertise on APSense
This advertising space is available.
Post Your Ad Here
Post Your Ad Here
Comments