How Google Relates to Image Generation

AI opens up new possibilities for creating images, text, and multimedia. However, Google emphasizes that it is important not only to use such technologies but to do so responsibly, with attention to quality and content accuracy.
Sources:
Google Assessor Guidelines 2025
Guide from Google Search Specialists on Using AI‑Generated Content https://developers.google.com/search/docs/fundamentals/using-gen-ai-content
A couple of our blog articles: SEO Optimization, Content for medical websites
1. Image Generation and Google Search Policies
Google allows the use of generative AI to assist in creating content — for example, to find information, organize data, or generate illustrations. However, if a website owner publishes many automatically created pages without adding original value for the user, this may be considered abuse of scalable content — a violation of Google’s spam policies.
In other words, if AI-generated content (including images) does not improve user experience and lacks unique quality or meaningful value, Google may lower such pages in search rankings.
2. Core Principles — Accuracy, Quality, and Relevance
Excerpt from Google’s guidelines: “If you create images or other materials using AI, pay attention to accuracy, quality, and relevance.”
In other words, an image should be high-quality and help users understand the content. Especially important:
Fill in metadata correctly, including
altandtitletext for images.Use structured data (Schema.org, etc.) according to Google’s standards.
2.1 Reflecting on Image Quality
Before publishing visual content created with AI, ensure it meets Google’s quality standards and does not mislead users.
Check the following:
No artifacts or errors. Make sure there are no extra elements — additional hands, fingers, distorted body parts, or unrealistic fragments.
Technical accuracy. If the image illustrates a process (e.g., repair, medical procedure, product assembly), make sure the correct actions, tools, and steps are shown.
Visual authenticity. Materials and details should be realistic. For example, a dental implant should have the correct shape, proportions, and texture.
Ethical limitations. AI‑generated images must not be used to represent company employees, clients, or real people. This could mislead users and violate Google’s transparency policy.
? Tip: Before uploading an image, use quality analysis tools (e.g., artifact or metadata checks) and add proper descriptions and ALT tags.
3. Recommendations on What Not to Do
Google strongly recommends disclosing to users how content was created. Excerpt from the guide: “If materials are generated automatically, disclose this to users in an appropriate way.”
This approach increases user trust and helps Google’s algorithms correctly understand the origin and purpose of the content.
3.1 When Disclosure Is Appropriate
Revealing that content is AI-generated can seem risky — essentially admitting the use of automation. However, in some cases, it’s appropriate and even beneficial for building audience trust.
3.2 When AI Disclosure Helps the User (YMYL Topics)
In niches related to YMYL (Your Money or Your Life — health, finance, safety, etc.), transparency is crucial. If AI usage may have influenced advice, recommendations, or data interpretation, it’s worth mentioning. Such disclosure helps build credibility and aligns with Google’s E‑E‑A‑T principles (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness).
3.3 When Disclosure Is Not Necessary
If AI was used as an auxiliary tool — for example, to simplify copywriting, technical descriptions, product cards, or articles about repairs or construction — explicit disclosure brings no added value to the user. Especially when the text is carefully edited and supplemented manually. In such cases, the quality, accuracy, and usefulness of the material matter more than its origin.
When in doubt, manually refine the text to ensure it meets quality standards.
4. Rule from the Assessor Guidelines (Section 4.6.6)
Google clearly states in the Search Quality Evaluator Guidelines, Section 4.6.6 that content created with little to no effort — including text, images, audio, or video — and lacking original value for users should receive a very low quality rating. This applies to materials that are copied, automatically generated, or rephrased without adding new value for visitors.
Even if the source is cited, pages without unique input or insight are rated poorly. Therefore, it’s important not just to use AI but to enhance generated content with original analysis, comments, explanations, and context.
5. Our Case: Replacing AI‑Generated Images with Real Ones
Our stance on imagery is clear: we stand for authenticity — genuine, truthful photos without Photoshop or AI generation. Sometimes we even organize professional photo sessions ourselves. Such images can be reused across the website and should always be prioritized by copywriters when illustrating articles.
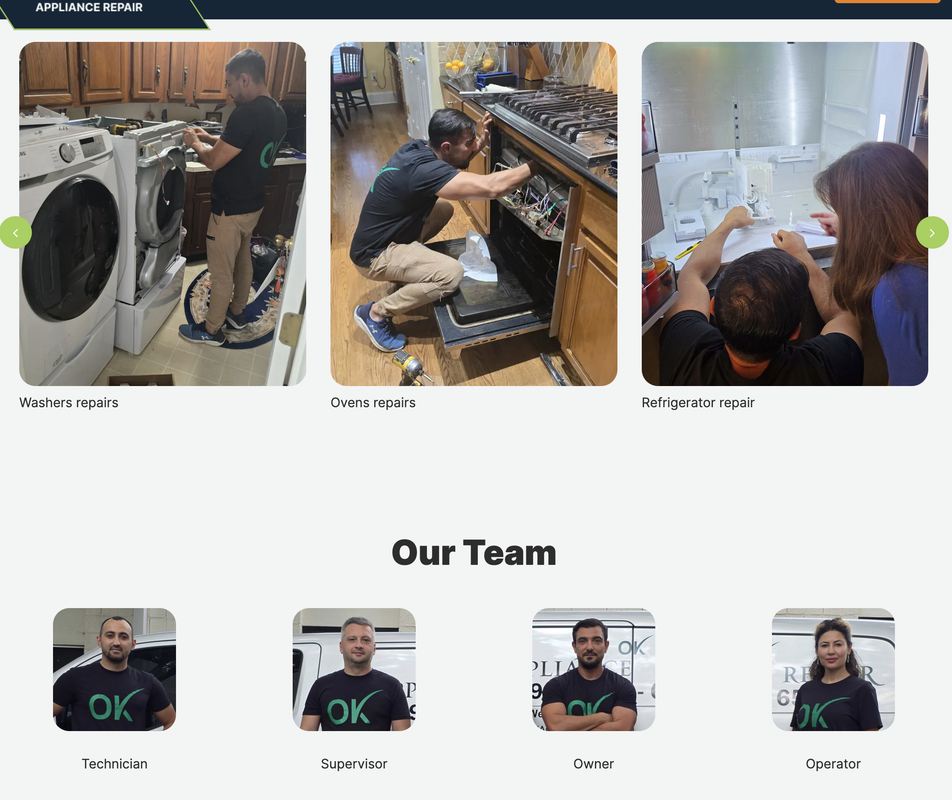
A client came to us with a website where sections like “Team” and “Work Stages” used AI‑generated employee photos. We recommended holding a real photoshoot to replace them with authentic pictures of the actual staff.
The case study is based on a home appliance repair company in Charlotte. The business repairs washing machines, microwaves, dryers, ovens, and stoves. Repairs are performed in clients’ homes, so it’s crucial for users to see who will come to their house. When visitors can view real faces, names, experience, and company branding, trust increases significantly. The site effectively introduces visitors to the technicians in advance.
Before

After
Additionally, authentic photos boost engagement, CTR, and conversion rates, as confirmed by analytics from the updated site.
Now, the “Team” section showcases real professionals, and the website looks far more trustworthy.
Conclusion
Google does not prohibit using generative AI to create images or text — but expects authors to maintain transparency, accuracy, and added value.
The key rule is simple: “Use AI as a tool, not a replacement for originality.”
If you create content that truly helps users, Google will support it. But if you publish large amounts of low‑value, repetitive AI‑generated material, search algorithms may treat it as spam.
Post Your Ad Here