what is a digital signature? how to get DSC, benefits, DSC classes 1,2 & 3?
what is a digital signature? how to
get DSC, benefits, DSC classes 1,2
& 3?

A computerized mark is a numerical procedure used to approve the legitimacy and honesty of a message, programming, or advanced report. It's what could be compared to a written by hand signature or stepped seal, however, it offers undeniably more inborn security. A computerized mark is planned to take care of the issue of altering and pantomiming in computerized correspondences.
Computerized marks can give proof of the beginning, personality, and status of electronic archives, exchanges, or advanced messages. Endorsers can likewise utilize them to recognize informed assent.
The following is an example of a signature line.
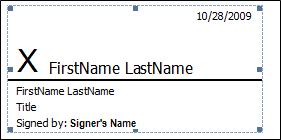
The role of digital signatures
In numerous locales, including portions of North America, the European Union, and APAC, advanced marks are viewed as legitimately restricting and hold similar worth as customary record marks.
Notwithstanding advanced record marking, they are likewise utilized for monetary exchanges, email specialist co-ops, and programming appropriation, regions where the legitimacy and respectability of advanced interchanges are urgent.
Industry-standard innovation called public key framework guarantees a computerized mark's information validness and respectability.
How do digital signatures work?
Digital signature assurances
The following terms and definitions show what assurances are provided by digital signatures.
Authenticity The signer is confirmed as the signer.
Integrity The content has not been changed or tampered with since it was digitally signed.
Non-repudiation Proves to all parties the origin of the signed content. Repudiation refers to the act of a signer denying any association with the signed content.
Notarization Signatures in Microsoft Word, Microsoft Excel, or Microsoft PowerPoint files, which are time-stamped by a secure time-stamp server, under certain circumstances, have the validity of a notarization.
To make these assurances, the content creator must digitally sign the content by using a signature that satisfies the following criteria:
The digital signature is valid.
The certificate associated with the digital signature is current (not expired).
The signing person or organization, known as the publisher, is trusted.
Important: Signed documents, which have a valid time stamp, are considered to have valid signatures, regardless of the age of the signing certificate.
The certificate associated with the digital signature is issued to the signing publisher by a reputable certificate authority (CA).
What are the benefits of digital signatures?
Security is the main benefit of digital signatures. Security capabilities embedded in digital signatures ensure a document is not altered and signatures are legitimate. Security features and methods used in digital signatures include the following:
- Personal identification numbers (PINs), passwords, and codes. Used to authenticate and verify a signer's identity and approve their signature. Email, username, and password are the most common methods used.
- Asymmetric cryptography. Employs a public key algorithm that includes private and public-key encryption and authentication.
- Checksum. A long string of letters and numbers represents the sum of the correct digits in a piece of digital data, against which comparisons can be made to detect errors or changes. A checksum acts as a data fingerprint.
- Cyclic redundancy check (CRC). An error-detecting code and verification feature is used in digital networks and storage devices to detect changes to raw data.
- Certificate authority (CA) validation. CAs issue digital signatures and act as trusted third parties by accepting, authenticating, issuing, and maintaining digital certificates. The use of CAs helps avoid the creation of fake digital certificates.
- Trust service provider (TSP) validation. A TSP is a person or legal entity that performs validation of a digital signature on a company's behalf and offers signature validation reports.
Other benefits of using digital signatures include the following:
- Timestamping. By providing the data and time of a digital signature, timestamping is useful when the timing is critical, such as for stock trades, lottery ticket issuance, and legal proceedings.
- Globally accepted and legally compliant. The public key infrastructure (PKI) standard ensures vendor-generated keys are made and stored securely. Because of the international standard, a growing number of countries are accepting digital signatures as legally binding.
- Time savings. Digital signatures simplify the time-consuming processes of physical document signing, storage, and exchange, enabling businesses to quickly access and sign documents.
- Cost savings. Organizations can go paperless and save money previously spent on the physical resources and on the time, personnel, and office space used to manage and transport them.
- Positive environmental impact. Reducing paper use also cuts down on the physical waste generated by paper and the negative environmental impact of transporting paper documents.
- Traceability. Digital signatures create an audit trail that makes internal record-keeping easier for businesses. With everything recorded and stored digitally, there are fewer opportunities for a manual signee or record-keeper to make a mistake or misplace something.
Importance of DSC for Fulfilling Statutory Compliances
Classes and types of digital signatures
There are three different classes of digital signature certificates (DSCs):
- Class 1. Cannot be used for legal business documents as they are validated based only on an email ID and username. Class 1 signatures provide a basic level of security and are used in environments with a low risk of data compromise.
- Class 2. Often used for electronic filing (e-filing) of tax documents, including income tax returns and goods and services tax (GST) returns. Class 2 digital signatures authenticate a signer's identity against a pre-verified database. Class 2 digital signatures are used in environments where the risks and consequences of data compromise are moderate.
- Class 3. The highest level of digital signatures, Class 3 signatures require a person or organization to present in front of a certifying authority to prove their identity before signing. Class 3 digital signatures are used for e-auctions, e-tendering, e-ticketing, court filings, and in other environments where threats to data or the consequences of a security failure are high.
Uses for digital signatures
Industries use digital signature technology to streamline processes and improve document integrity. Industries that use digital signatures include the following:
- Government. The U.S. Government Publishing Office (GPO) publishes electronic versions of budgets, public and private laws, and congressional bills with digital signatures. Digital signatures are used by governments worldwide for a variety of reasons, including processing tax returns, verifying business-to-government (B2G) transactions, ratifying laws and managing contracts. Most government entities must adhere to strict laws, regulations and standards when using digital signatures. Many governments and corporations also use smart cards to ID their citizens and employees. These are physical cards endowed with a digital signature that can be used to give the cardholder access to an institution's systems or physical buildings.
- Healthcare. Digital signatures are used in the healthcare industry to improve the efficiency of treatment and administrative processes, to strengthen data security, for e-prescribing and hospital admissions. The use of digital signatures in healthcare must comply with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) of 1996.
- Manufacturing. Manufacturing companies use digital signatures to speed up processes, including product design, quality assurance (QA), manufacturing enhancements, marketing and sales. The use of digital signatures in manufacturing is governed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Digital Manufacturing Certificate (DMC).
- Financial services. The U.S. financial sector uses digital signatures for contracts, paperless banking, loan processing, insurance documentation, mortgages and more. This heavily regulated sector uses digital signatures with careful attention to the regulations and guidance put forth by the Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce Act (E-Sign Act), state Uniform Electronic Transactions Act (UETA) regulations, the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) and the Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council (FFIEC).
- Cryptocurrencies. Digital signatures are also used in bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies to authenticate the blockchain. They are also used to manage transaction data associated with cryptocurrency and as a way for users to show ownership of currency or their participation in a transaction.
- When an importer has to clear his shipments from the customs then it’s needed by the customs authorities.
- When an importer sends money abroad through banks then it’s needed by the bank.
- When an exporter has to send his shipments then it’s needed by the customs port.
- When an exporter receives money in foreign currency directly into his bank account then it’s required by the bank.
Benefits of IEC Registration
Expansion of Business
Availing Several Benefits
No Filing of Returns
Easy Processing
No Need for renewal
Validity of IEC
The Duplicate copy of the IEC
Surrender of IEC
Modification in IEC
Post Your Ad Here


Comments