The ABCs Of Heat Recovery Home Ventilation Systems
In the contemporary world, homes are constructed in sophisticated designs and systems unlike the past models which are a little outmoded. Modern homes are much more efficient in terms of energy conservation courtesy of improved heating solutions. An important upgrade that has happened is the invention of insulation techniques that keep houses airtight so that heat is retained for long. However, there is an obstacle to this technique which is poor ventilation in the houses. Wet areas like bathrooms and washing areas can stay damp if not properly ventilated and this poses a lot of health hazards. If moisture level in a house is not controlled, a lot of problems start to show up: asthma risks, dust mites, molds, and mildew. Windows and doors can be opened to let in fresh air but the practice is not effective during cold seasons as in may increase the heating bills of the house as cold air gets in.
Definition
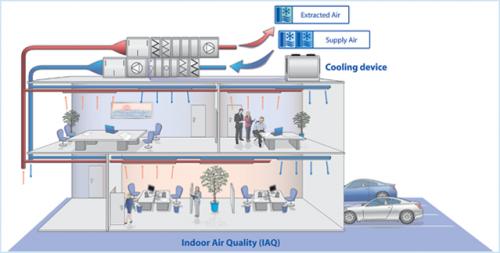
Heat recovery ventilation systems are basically ducts which run side by side and mounted on both the interior and exterior sides of a house. One duct takes in fresh air into the house while the other conducts stuffy air out of the house. The air passes through heat exchanger whose function is to allow outgoing air to exchange its heat with the air flowing in. The two airflows do not get mixed up during heat exchange. Every duct contains a fan that turns up or down as the temperatures change.
How it works
A house contains damp and hot air which flows out to give away its heat to the incoming air. In this system, no heat loss occurs during the counter flow. Large houses require ventilation grids for every room in the house to feed into the ducts running between floors and join to one channel outside the house.
The difference between Heat Recovery Ventilation (HRV) Energy Recovery Ventilation (ERV)
Ventilation systems work differently. ERV is a alterative system for HRV although it transmits a percentage of moisture from the air flowing out to the one coming in. This creates a balanced humidity condition in the house. It is crucial for home owners who don’t prefer total dry environments. Ideally, ERV is more efficient in humid climatic regions but with air conditioning. ERVs reduce interior moisture which can lead to heat loss and more energy bills, so, it is cost-effective. HRV on the other hand, is more suitable where no air conditioning exists or if the environment is drier and less humid.
Merits of HRV
HRV systems provide fresh air into a warm house. They are very effective in reducing power bills during winter since you don’t need to open doors and windows for air freshening. During summer, HRV minimize air conditioning costs since they kick out humidity out of the house. They also maintain good condition of house furniture and walls by eliminating excess humidity.
Demerits of HRV
On the negative side of HRV, the cost of installation is very high and they do not guarantee to cover up for their installation expense in the long run. The major benefits are reaped during adverse weather conditions when the inside and outside conditions differ considerably. When the climate is moderate, the advantages are less or null in some instances. To run the system, additional costs of maintaining fans is incurred. Unless you are an environmentalist and rich, you may not save much on money and energy with these ventilation systems. For those who live in extremely cold regions, they will need more complex devices that will prevent freezing of the ventilation ducts. Finally, HRV require constant check-ups since the air filters need to be washed or replaced after at least every 6 months.
Post Your Ad Here

Comments