Access to Optimum Antibody Labeling Results
Why Antibody Labeling
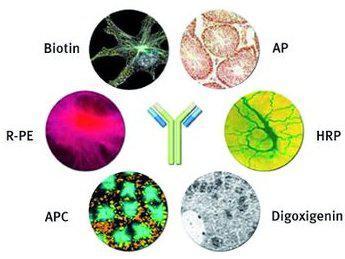
In order to visually see the antigen–antibody immune-reaction (with or without tools, such as microscope), the antibody should take a label –Fluorophores, Nanoparticle, Biotin, Enzyme, Oligonucleotide, Liposome.
The Choice of Labels
Fluorophores, such as FITC, TRITC, DyLight Fluors, green fluorescent protein (GFP), R-Phycoerythrin, AMCA dyes, etc., can be directly visualized in a fluorescent microscope.
Nanoparticle, such as nanogold, colloidal gold, nanocrystal, etc., can be visualized in the electron microscope without further treatment.
Biotin, such as avidin, Biotin, streptavidin, etc., can be visualized in light, fluorescence and electron microscopy in combination with ABC technique
Enzyme, such as HRP, AP, Beta--galactosidease, etc., can be visualized in the light microscope
Oligonucleotide enables highly sensitive immunoassay
Liposome has become more and more popular.
Antibody Labeling, “Direct” or “Indirect”
The labels in an immunoassay are either ‘direct’ or ‘indirect’ detection of the antigen. Here we summed advantages & disadvantages of the two methods:
Direct is a quick methodology since only one antibody is used and its non specific binding of secondary antibody is eliminated. However, the immunoreactivity of the primary antibody may be reduced as a result of labeling. It has little signal amplification.
Indirect’s sensitivity is increased because each primary antibody contains several epitopes that can be bound by the labeled secondary antibody and it allows for signal amplification. However, its non specific binding may occur with the secondary antibody and it needs extra incubation and wash steps.
Antibody Labeling Methods
There are many labeling procedures as we may find either in literature or in reality. But generally speaking, some of them are just having variant names; they are actually the same in nature. Here we listed four common approaches to labeling, as following:
NHS esters
Heterobifunctional reagents
Carbodiimides
Sodium periodate
Key Considerations for Antibody Labeling
During the process of antibody labeling, there are some important considerations to take into account. Here are four steps that you may want to know:
1. Select a proper label for the target application
With regard to factors such as absorbance, emission and extinction coefficient, the correct fluorescent label is vital.
2. Check purification, buffers and additives
Once settled the first step (a suitable label) for the conjugation, remember to make sure that the substances within the antibody formulation will not affect the conjugation process.
3. Keep the amount of antibody in mind
It’s important to avoid over-labeling or under-labeling since both will lead to the inability of antibody-antigen bind.
4. The way stores the new conjugate
Upon the newly labeled antibody, the next is storage for use if not now. Therefore reading the construction of storage conditions is of high importance to ensure they are compatible with give settings.
Should the antibody labeling nevertheless be desirable, one can use Creative Diagnostics’ Antibody Labeling Service and Antibody Fragmentation Service. At Creative Diagnostics, we use innovative to enables direct and quick labeling of antibodies for use in R&D applications, drug discovery and the development of diagnostic kits. Our service is efficient and confidential, and we guarantee the quality of our work.
Post Your Ad Here
Comments