What is thin endometrium? symptoms causes and treatment
The thin endometrium is the tissue that lines the inner layer of the uterus and is essential for reproduction because embryo implantation takes place here. For a successful pregnancy, the embryo must attach itself to the endometrial lining. There are two hormones (Oestrogen and Progesterone) that help in preparing and thickening the endometrial lining for implantation. As the pregnancy progresses, all the nourishment that is required for the growth of a baby is supplied by the glands present in the uterine lining. And in the absence of a proper thick endometrial lining, it would be difficult to hold a pregnancy.
What is thin endometrium or a thin lining of the womb?
The uterus is lined with three layers. The outer lining is called serosa, the middle layer myometrium and the innermost lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. The endometrium lining keeps changing throughout the menstrual cycle. For an Embryo to go and implant in the endometrium, it should be in an optimal condition that is, and it should be thick with a good blood supply.
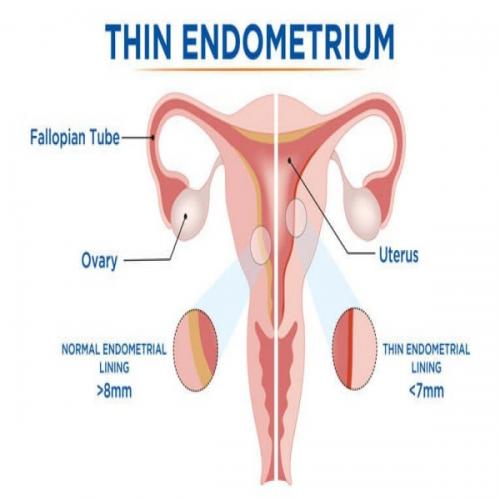
When a woman is undergoing an IVF cycle, her endometrial lining is routinely measured through transvaginal ultrasound. Because an endometrium thickness of 8 mm or above is considered normal for successful embryo implantation, a thickness of less than 7 mm is considered a Thin Endometrium and having thin uterine lining symptoms, may decrease the chances of a successful pregnancy. And if the endometrium lining is less than 5 mm, then there is no chance of pregnancy.
What are the thin endometrium symptoms?
Females who have thin uterine lining can have some issues, as the thin endometrium symptoms or the symptoms of the thin uterine lining, pertaining to:
*Infertility – Women who have thin uterine lining may have fertility issues, as a healthy endometrium with proper thickness is needed for implantation and growth of the foetus.
*Abnormal Menstrual Cycle – They may also have an abnormal menstrual cycle which may include:
*Painful periods –Periods may be accompanied by pain and is one of the common symptoms of thin endometrium.
*Irregular timings of periods – The timings of the menstrual cycle are irregular and pose to be the possible signs of the thin uterine lining.
*Reduced menstrual bleeding – This is also one of the symptoms of a thin uterine lining. Menstrual bleeding lasts for a lesser time than usual because the endometrial lining that is needed to be shed off is very thin and has fewer issues that need to be flushed out during the time of menstruation.
*Asymptomatic – Many times, they can be no symptoms of thin endometrium and detected on ultrasound.
What are the causes of thin endometrium?
*Low Oestrogen –Oestrogen hormone is necessary for the thickening of the endometrium and a woman who has thin endometrial lining may have a low oestrogen level. In this case, medication with oestradiol is prescribed, and its response is monitored. If the endometrial lining doesn’t thicken, then it may indicate that the blood supply is inadequate or there has been some damage to the tissues of the uterine wall.
*Inadequate Blood Flow – There are a lot of reasons for inadequate blood flow to the uterus. A woman who leads a sedentary lifestyle may have reduced blood flow, causing the endometrial lining to shrink. If a woman has a tilted uterus then also it will receive less blood supply. The presence of fibroids, polyps also constricts the blood vessels, thus reducing blood flow to the endometrial lining.
*Poor Health of Endometrial Tissue – Any kind of bacterial infection like endometrial TB, sexually transmitted diseases and pelvic inflammatory diseases can cause inflammation which can scar the endometrial lining.
*D & C or any Surgeries – Many a time during dilation and curettage the functional basal layer of endometrium called basalis is removed, in this case, the new endometrial lining cannot grow, and the endometrium stays thin, this is called Asherman Syndrome and is difficult to treat.
*Birth Control Pills – Women who take birth control pills for a long time, can have a non-functional and thin endometrial lining. Oral contraceptive pills are a combination of oestrogen and progesterone and whose overuse or withdrawal can result in changes in oestrogen level and the endometrial lining.
*Clomid – These drugs are administered to stimulate ovulation. Excessive use of Clomid can cut off oestrogen supply, because of which the endometrium lining cannot grow in thickness.
Is pregnancy possible with thin endometrium?
A thin endometrium has been associated with implantation failures or can lead to early miscarriages (Miscarriage Meaning in Hindi) due to lack of blood supply. If a woman has been facing fertility issues or having recurrent thin uterine lining miscarriage, a doctor might ask to get her oestrogen level, and endometrial thickness checked. For successful implantation of an embryo or successful pregnancy with a thin uterine lining, the uterine lining should be more than 8mm. An endometrial thickness < 7 mm is associated with a lower probability of pregnancy. So, for a successful pregnancy with a thin uterine lining, it is seen that hormone replacement therapy (HRT) and frozen embryo transfer (FET) has given better outcomes due to improved endometrial receptivity. The endometrial receptivity of endometrium can be checked through a molecular diagnostic test which helps to locate the implantation window, so a personalized embryo transfer can be done to reduce the chances of implantation failure.
What are the treatment options for thin endometrium?
For a successful pregnancy, a thin endometrial lining should be properly evaluated and treated accordingly to make it thick and nourishing so that it can accept an embryo. A doctor would treat a patient based on the diagnosis of the problem. It can be managed both medically and naturally. Some of the thin uterine lining treatment methods are discussed below.
*Oestrogen Therapy – As already discussed a decrease in the oestrogen level may cause the endometrial lining to thin. In this case, oestrogen can be given orally or as a suppository gel, as it stimulates the division of cells in the endometrial lining so that it becomes thick and the fertilised egg can go and implant easily.
*Indirect Oestrogen Therapy – Women who are trying to conceive can be given human Menopausal Gonadotropin (hMG) so that it stimulates the pituitary gland to release the gonadotropin hormone. This will trigger the reproductive organs to release the oestrogen hormone, which will help the uterine lining to become thick.
*Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) – Newer techniques like an Intrauterine infusion of this (G-CSF) growth hormone has been seen to increase the thickness of the endometrial lining.
*Hysteroscopy – If any intrauterine adhesions are responsible for the uterus lining thin, then through hysteroscopy, the scar tissues or adhesions can be removed which can eventually cause the endometrial lining to grow to its appropriate thickness.
*Frozen Embryo Transfer (FET)– If during an IVF cycle it is found that a patient has a poor endometrium, then the best way would be to freeze all her embryos in that cycle, and transfer once the endometrium has thickened and is ready to accept the embryos.
*Natural Treatment – Some natural supplements and herbs, vitamins like Vit E and L-arginine, regular exercise, acupuncture and fertility massage have been shown to improve the thickness of the endometrium, by improving blood flow to the uterus.
Advertise on APSense
This advertising space is available.
Post Your Ad Here
Post Your Ad Here
Comments