Applying clean coal technology
by Rudy P. SysAdmin at howtofindthemoneyClean coal technology
A new generation of coal-burning power plants with energy processes that reduce air emissions and other pollutants.
Coal power plants technology must adapt to the changing political climate towards environmental issues.
Clean coal technologies are several generations of technological advances that have led to more efficient combustion of coal with reduced emissions of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide.
- Wet scrubbers
- Integrated Gasification Combined Cycle (IGCC)
- Flue Gas Desulfurization
- Low Nitrogen Oxide (NOx) Burners
- Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR)
- Electrostatic Precipitators
- Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)
1. Wet scrubbers
When the emissions reach the flue of the furnace limestone and water are sprayed
The SO2 reacts with the calcium carbonate (limestone) to form gypsum (calcium sulfate). The gypsum is collected and used for construction.
2. Integrated Gas Combined Cycle (IGCC)
IGCC uses a coal gasification system to convert coal into a synthesis gas (syngas) and produce steam.
- The hot syngas is processed to remove sulfur compounds, mercury and particulate matter before it is used to fuel a combustion turbine generator, which produces electricity.
- The heat in the exhaust gases from the combustion turbine is recovered to generate additional steam
- This steam, along with that from the syngas process, then drives a steam turbine generator to produce additional electricity.
The integration of these technologies provides the high efficiency of the combined-cycle design with the low cost of coal
Integrated Gas Combined Cycle (IGCC) advantages:
- Efficiencies currently approaching 50%, IGCC power plants use less coal and produce much lower emissions of carbon dioxide than conventional power plants
- Higher output: Using syngas in a gas turbine increases its output
- The gasification process in IGCC enables the production of not only electricity, but a range of chemicals, by-products for industrial use, and transport fuels
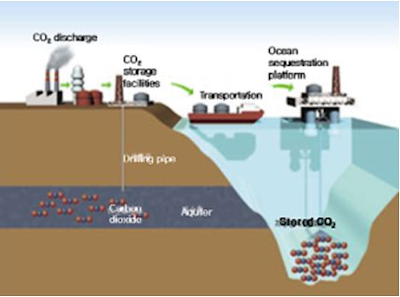
3. Carbon capture and storage
Process consisting of the separation of CO2 from industrial and energy-related sources, transport to a storage location and long-term isolation from the atmosphere.
Three processes in the CCS technology
- Capturing the CO2 produced from industrial or power generation processes
- Transporting the CO2 to an underground geological formation which is suitable geological formations
- CO2 can be used as fluid in “Enhanced Oil Recovery”, where CO2 pushing the remaining oil.
The CO2 is grabbed after the fossil fuel is burned. The burning of fossil fuels produces something called flue gases. In a post-combustion process, CO2 is separated and captured from the flue gases that result from the combustion of fossil fuel
CO2 is trapped before the fossil fuel is burned. That means the CO2 is trapped before it's diluted by other flue gases. Coal, oil or natural gas is heated in pure oxygen, resulting in a mix of carbon monoxide and hydrogen. This mix is then treated in a catalytic converter with steam, which then produces more hydrogen, along with carbon dioxide.
The power plant burns fossil fuel in oxygen. This results in a gas mixture comprising mostly steam and CO2. The steam and carbon dioxide are separated by cooling and compressing the gas stream.
Gasification
the process of producing syngas–a mixture consisting primarily of methane (CH4) carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H2), carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor (H2O)–from coal and water, air and/or oxygen.
Coal gasification reaction
In coal gasification, four principal reactions are crucial:
- Steam gasification
- Carbon dioxide gasification
- Hydrogasification
- Partial oxidation reaction
The steam gasification reaction is endothermic.
Carbon dioxide reacts with carbon to produce carbon monoxide and this reaction is called Boudouard reaction. This reaction is also endothermic in nature, similar to the steam gasification reaction.
Direct addition of hydrogen to coal under high pressure forms methane. This reaction is exothermic and requires high temperature and pressure.
Combustion of coal involves reaction with oxygen, which may be supplied as pure oxygen or as air, and forms carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide. Principal chemical reactions between carbon and oxygen involve:
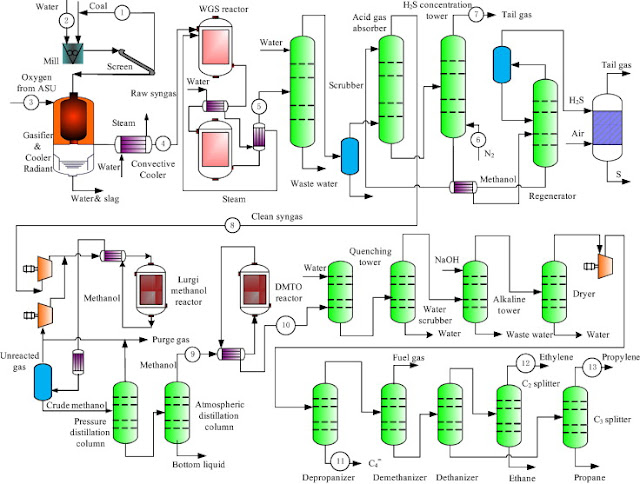
Coal to chemical (CTC)
Coal to olefins technology
Olefins are one of the most important oil derivatives widely used in industry.
To reduce the dependence of olefins industry on oil a number of coal-to-olefins (CTO) processes have been developed:
- UOP/Hydro MTO
- DMTO developed by Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics of Chinese Academy of Science
- SMTO by Sinopec
- Lurgi MTP
- FMTP by Tsinghua University
A CTO plant based on the technology was built by Shenhua Group and successfully put into commercial production on January 2011 with capacity 0.7 Mt/a olefins (0.3 Mt/a ethylene, 0.3 Mt/a propylene, and 0.1 Mt/a C4 ).
Coal to liquid fuel (Coal liquefaction)
Coal to liquid fuel
Fischer-Tropsch process
Converting a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide—derived from coal, methane or biomass—to liquid fuels uses hydrogen (H2) and carbon-monoxide (CO) to make different types of hydrocarbons with various H2:CO ratios
In a CTL facility the H2 and CO can be supplied from the coal gasifier.
Cobalt ------------- Alkanes
Nickel ------------- Methane
Ruthenium ------- High molecular weight hydrocarbons
Rhodium ---------- Large amounts of hydrocarbons & little oxygenates
Source: Rama Oktavian
Sponsor Ads
Created on Jul 25th 2019 05:49. Viewed 567 times.