A Comprehensive Guide to Genital Wart Cure
by Chris G. Work in Internet Business industryGenital warts are a sexually transmitted infection common in the U.S. and can cause discomfort, embarrassment, or pain for those who contract it. Genital warts are caused by human papillomavirus (HPV), present in about 20% of the population. Genital warts can be cured with either medication or surgery; both methods have benefits and drawbacks. This article will cover everything you need to know about genital wart cure, including treatment options, symptoms, prevention tips, and more!
What Causes Genital Warts?
Genital warts are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV) infection. The virus invades and grows in your body's sexual organs, which can lead to symptoms such as itching or pain during sex for some people who have it -- or even just a high-risk factor due to their lifestyle choices. Genital warts can be caused by many things, including infection, poor hygiene, and even wearing tight pants.
The most common way to develop is through contact with an infected person's fluids such as sweat or blood during sex without using protection from STDs ( Sexually Transmitted Disease). An overview of how the virus enters our body is absorbed in minor cuts made while touching something dirty like public transportation. If there isn't already some antigen vaccine available, we'll contract this potentially life-threatening illness that can cause genital warts.
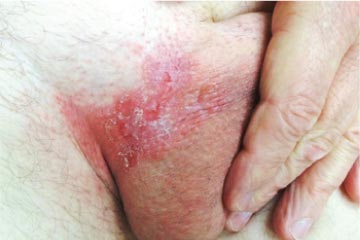
Symptoms:
Currently, two types of Genital Warts can be treated. The most common variant occurs in women and causes no discomfort or pain on its own; however, if left untreated, then symptoms may include small puckering bumps around your genital area with an asymmetrical appearance due to crowding out from other healthy cells nearby (this goes away after treatment). Another form called inguinal cervical type has been reported less frequently than in previous decades. Still, it exists because afflicted individuals tend to have multiple verrucous carcinoma-like growths along this region's roof - also known as "the gold standard" among doctors who practice female anatomy persuasion.
Not everyone with genital warts will experience symptoms, but when present, symptoms can include:
-Itching or burning in the genital area
-Bleeding during intercourse
-Painful urination
-Genital warts that are visible to the naked eye
Treatment Options:
There are a few different methods of genital wart treatment that can be used to combat warts: over-the-counter medications, prescription medications, and surgery. Depending on your symptoms and preference, one method may be more suitable than another for you! Over-the-counter medications include Aldara (imiquimod), Condyline (podofilox), and Wartrol (sodium lauryl sulfate). These medications can be used to cure genital warts, but they should only be used if the warts are not too large or widespread. If the wart is more than 1 cm wide or has many warts, prescription medication such as Imiquimod cream, Podofilox liquid, and Sinecatechins ointment should be used instead. If the condition is extensive or not responding to other types of treatment, a doctor may suggest surgery.
The best genital wart cure methods will depend on how widespread the warts are and what your preference for treatment is. If you are looking for a fast cure with minimal side effects, over-the-counter medications may be best for you. However, prescription medication or surgery may be necessary if the warts are widespread or not responding to other treatment methods.
How Should You Prevent Spreading Genital Warts?
If you have genital warts, always wear a condom. Wear protection during sex and avoid smoking because it increases your chances of catching these pesky common infections that are more likely to return if you smoke; this is important for both partners in any relationship or single encounter alike! You should also let others know about the infection before having intimate contact so they can take necessary precautions as well, too - not just yourself (especially when we're talking about skinship!).
Most brands can protect against some types of virus, which cause most cases in males and females (HPV). If you find out that your partner has genital warts, it's essential to encourage them to see a doctor or nurse about the HPV vaccine. It is also necessary for people who have been vaccinated not to engage in sex until all symptoms are gone from their vaccinations, as there may still be remnants left behind after an infection goes away. Use condoms when engaging sexually because this helps reduce risk even more than usual during oral, anal, and vaginal intercourse.
How Long Does It Take to Cure Genital Warts?
Genital warts can last as long or as short a period, depending on the person. They typically go away after some time, but in some cases, they never do and may need removal by surgery to remove them entirely.
One way you can tell when these types of infestations will clear up is if there's no change over several weeks with regards whatsoever - this usually means one thing: you need a surgical intervention!
Genital Wart Relapses:
There is a chance that your genital warts will relapse, which means they may come back. This can happen when the virus in you dies off and then starts to grow again because of how much time has passed since the last outbreak or treatment session, for example - but not always! It's essential to stay optimistic about this situation; sometimes, people see their condition improve after one round with treatment, while others need more than two tries before seeing results (and some never do).
Genital warts can relapse after treatment with certain drugs, such as interferon. The virus that causes genital herpes also commonly spreads to one's mouth and eyes during an outbreak--a condition called "herpes simplex." This particular type cannot be distinguished from other types by sight alone, though, because they all look similar until there is enough viral buildup on surfaces like fingertips or eyelashes, which will result in small ulcers/lesions ("proliferation").
Genital Warts and Pregnancy:
Genital warts are a sexually transmitted disease that can lead to serious health problems. They often grow on the genitals, but sometimes they spread more than ten centimeters from where their initial infection occurred - so don't think you're safe just because it doesn't look like your doctor has found anything yet! Women who become pregnant still need treatment for these warts even though there is no risk whatsoever during pregnancy itself; once delivered, the baby gets spores themselves through contact with infected material near the mommy's vagina or anus region (groins). It's best if both partners receive annual pap tests which catch precancerous cells before they turn into full-blown cervical cancer.
If a pregnant woman contracts genital warts, there is the possibility that her baby could be infected as well. This usually happens because of contact with secretions or mucous membrane during unprotected sex, leading to direct skin-to-skin transmission in females. However, if someone has recently had their newborn, they may reinfect themselves while changing them, for example, when giving him his first bath.
The doctors are saying that there isn't any known treatment specifically designed only for people who have contracted this virus and carrying fetuses, so whatever we can do about prevention would help more than anything else at present. Luckily, we've come pretty far since anti-human immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV) medications were barely imaginable!
Sponsor Ads
Created on Dec 16th 2021 04:46. Viewed 252 times.



